In this tutorial we’ll continue with the serial communication between 2 microcontrollers. You should always configure one PIC as master while all the others are to be configured as slaves. For more information check this SPI explanation.
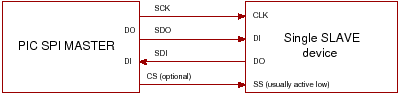
SPI Master-Slave Configuration
Check the datasheet to see which pins are SDO (output), SDI (input) and SCK (SPI Clock). Once you have connected the PICs there are a couple of registers that need to be set.
This is for the master:
MOVLW 0x00 ; Datasample middle, SCK act-idle. MOVWF SSPSTAT ; MOVLW 0x32 ; SSP enabled, Idle at high, Fosc/64 MOVWF SSPCON1 |
As you can see we use the internal timing components for the SPI clock, however you can opt to use TMR2 as well. Don’t forget to enable TMR2 and set its T2CON register if you do this.
This is for the slave:
MOVLW 0x00 ; Datasample middle, SCK act-idle. MOVWF SSPSTAT ; MOVLW 0x35 ; SSP enabled, Idle at high, SPI SLAVEMODE MOVWF SSPCON1 |
Make sure you don’t make a mistake here, if you have your CLK idle at high, see to it that the transition is configured correctly else you’ll miss the first pulse. For example, when the CLK is idle at high, its first pulse will be from high to low. When you configure the slave that it should do something when the CLK goes from low to high you will have missed that first pulse resulting in missed or incorrect data.
Now you have configured both master and slave you can send any data you wish. Let’s take a look on how to transmit data from master to slave:
Main goto Main ; Infinite loop SPIsend bcf PIR1,ADIF ; Clear AD converter flag MOVFF ADRESH,SSPBUF ; move ADRESH to send buffer RETURN SPIread bcf PIR1,SSPIF ; Clear the flag MOVFF SSPBUF,PORTB ; Move received data to PORTB RETURN inter ; using single interrupt priority BTFSC PIR1,SSPIF ; if set-> transmission finished CALL SPIread BTFSC PIR1,ADIF ; wait until AD finished -> send CALL SPIsend RETFIE END |
In this example I’m sending values sampled by the AD converter to the slave. The code is pretty self explanatory. The ADC will generate an interrupt when it’s finished with converting and the SPI will generate one when it’s done transmitting the data that was in SSPBUF, which is the send buffer.
The slave has even simpler code:
main goto main SPIread bcf PIR1,SSPIF movff SSPBUF,PORTA return inter BTFSC PIR1,SSPIF CALL SPIread RETFIE END |
The slave will generate an interrupt when the data byte is received, you just have to move the data in the buffer to another register such as PORTA if you’d like to display the data with LEDs for example.